Social Ecosystems
- Combatting Wildlife Crime (CWC) projects
- Community Based Natural Resource Management (CBNRM)
- Education and Lifestyle
Combatting Wildlife Crime (CWC) projects
INL2
Funding: USDOS, INL and WWF
Partners: SRT
Starting date: October 2017 to August 2022
Title: Combatting Wildlife Trafficking in Namibia
Contact person: Peter Erb This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Location: Field-based, southern Kunene and Erongo regions.
Objectives:
- Anti-Poaching and Counter-Trafficking Support: Support MET and NAMPOL nationally to implement on-the-ground anti-poaching interventions to deter and capture poachers.
- Investigations: Support MET and NAMPOL case officers to more effectively investigate poaching cases, penetrate trafficking syndicates, to effect better arrests and prepare better dockets for court. (WWF managed component)
- Prosecutions: Support prosecutors to more effectively prosecute poachers and members of criminal syndicates. (WWF managed component)
- Customs: Support Namibian Customs to improve interception rates for ivory, rhino horn, and other illegal wildlife products being smuggled through Customs.
- Rhino Custodians: Incentivize and support the active engagement of Namibia's Rhino Custodians.
- Support the NGOSS: Support the NGOs to guide civil society engagement in the fight against wildlife crime, promote lesson learning between LE practitioners, and leverage additional non-US Government funding.
- Support to Blue Rhino Task Team: Support Blue Rhino to further solidify the strategic partnership between the Intelligence and Investigations Unit (IIU) of MET and the Protected Resource Division (PRD) of NAMPOL and other law enforcement agencies. (WWF managed component)
INL3
Funding: USAID, INL and WWF
Partners: SRT
Starting date: September 2021 until 31 August 2023
Title: Combatting Wildlife Trafficking in Namibia
Contact person: Peter Erb perb@nnf,org.na
Location: Field-based, southern Kunene and Erongo regions.
Objectives:
- Support MET to implement on-the-ground anti-poaching interventions to detect, prevent, and reduce poaching activity in four operational areas (Etosha National Park, northwest communal areas, central and custodian, Kavango/Zambezi)
- Improve aerial support for MET and NAMPOL case officers
- Increase the capacity of Namibian law enforcement and customs officials to investigate transnational wildlife cases
- Empower national and regional wildlife law enforcement to build a sustainable foundation to better prevent, detect, and investigate wildlife crime through specialized training and assistance
CD-86 and CD-87
Funding: USDOS, INL and WWF
Partners: SRT
Starting date: October 2017 to August 2022
Title: Combatting Wildlife Crime in Namibia and the Kavango-Zambezi Area Project, USAID - AID-674-A-17-00002
Contact person: Peter Erb This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Location: Field-based, Kavango-Zambezi Regions.
CD-86 Objectives:
- The Flow and Linkage Between Viable Wildlife Populations and Community Benefits Strengthened (Benefits)
- Community Governance and Leadership of CBOs in Wildlife Management and Stewardship Enhanced (Governance and Stewardship)
- Community Pride in Wildlife Built (Awareness and Pride)
Outcome: Community Benefits, Stewardship, and Engagement in Combatting Wildlife Crime Improved (or Increased)
CD-87 Objectives:
- New approaches, tools, and technologies for field-based LE activities leveraged
- Anti-poaching and LE efforts strengthened and improved
- Information sharing among PA managers, LE officials, communities, and private sector supported
Outcome: Anti-Poaching and Surveillance Capacity and Collaboration Among Communities, Private Sector, and PA and LE Officials Strengthened
Completed Projects
GIZ PoliFund - Partnership Against Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade
Funding: Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Internationale Zusammenarbeit
Starting date: 1 April 2019 – 1 March 2021
Title: Developing an Integrated Wildlife Crime Communications Platform
Contact person: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Location: Namibia
Project Background
Wildlife crime is ongoing in Namibia, but more recently there have been some major efforts to strengthen the response to this scourge. These efforts have focused on prevention, response, and follow-up but comparatively little has progressed around communications. Although it is accepted that poaching has decreased slightly in 2016 and 2017 no figures are readily available, nor is there any coordinated communication on arrests, prosecutions, and sentences handed down to poachers. This is in itself part of the challenge that the project aims to address. In addition, whilst there has been a concurrent increase in coverage of poaching issues in the national and international press, there has been little in the way of any concerted media outreach campaign targeting identified segments of the population. Furthermore, despite increased coverage, the media in Namibia do not comprehensively or consistently report environmental topics with the aim to interpret the technical and or political complexities for the public to easily understand and take informed actions for environmental protection in Namibia.
Objectives: The project aims at building up public awareness of the issues related to wildlife crime by developing a national feeling of pride and resilience around key species and Namibia's wildlife populations in general. The intervention will focus primarily on two critical voices and the creation of a neutral platform to drive more coherent communications through the Ministry of Environment and Tourism and rural communities.
The overall outcome should be a sustainable coalition that drives public awareness, targeted advocacy, and peer pressure to help change knowledge, attitudes, and behavior towards wildlife crime and support conservation efforts.
USAID - WCS
Funding: United States Agency for International Development (USAID) through the WWF Namibia
Partners: WWF, NACSO, IRDNC, SRT, MET
Starting date: 2017
Title: Combating wildlife crime in Erongo and Southern Kunene regions of Namibia
Contact person: info@nnf,org.na
Location: Field-based, southern Kunene and Erongo regions.
Project Background
Rhino poaching in the South Kunene and Erongo regions of Namibia, home to the only truly wild Black Rhino population outside of protected areas in the world, has increased over the years.
This project provides support to community game guards working in communal conservancies in terms of anti-poaching and wildlife crime mitigation efforts. This support is closely coordinated with ongoing anti-poaching and law enforcement efforts as well as new support mechanisms that have commenced in 2017/18. In this respect, project staff play a facilitating and coordinating role between target communities, the natural resource working group (NRWG), other NGOs, and MET working in the target area. Additionally, the project advances iconic species conservation with a focus on rhino conservation and monitoring. Through the development of diversified tourism activities around rhino tracking, payment schemes for elephant sightings, and exploration of associated payments for ecosystem services in this unique landscape.
At the community level, the promotion of active reporting of suspicious activities and development and pursuit of the appreciative inquiry concept with conservancies will raise awareness of wildlife and ecosystem values. This process will ultimately enhance community pride and resilience.
Project outcomes will be in line with the Namibian Government’s newly developed ‘National Strategy to Combat Wildlife Crime’. The NNF will pilot an open innovation approach, and the experience of dealing with poaching against a background of high inequality and rising deprivation will be widely documented and made available to organizations in other countries through various CBNRM fora.
USAID VukaNow
Funding: United States Agency for International Development (USAID)
Starting date: 1 July 2019 – 1 August 2020
Title: Strengthening Blue Corridors and Building Pride to Combat Wildlife Crime
Contact person: info@nnf,org.na
Location: Along the NE Rivers – Zambezi and Chobe Rivers
Project Background
Component One: The transboundary rivers of KAZA are the lifeline of the region for both people and wildlife. They are also conduits for movement. Previous projects on fisheries management, implemented by the NNF and its partners, revealed the nature and extent of the shared fish resources. In Namibia, a decline in river fisheries over the last 3-5 years was concealed by the highly productive ephemeral Lake Liambezi that received inflow. The highly productive lake encouraged the commercialization of fishery in the region and opened trade routes into the copper belt of Zambia and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Nationals of all three countries developed sophisticated business relationships. As the productivity of Lake Liambezi declined and the lake dried up, the paucity of fish in the rivers resulted in more destructive fishing methods to meet the demand and maintain business operations. This led to the collapse of river fisheries, heavily impacting the livelihoods of people and communities who have traditionally fished the rivers.
Objective One: To strengthen riverine communities, a critical line of defense against wildlife crime and illegal wildlife trafficking, we intend to (1) encourage the implementation of fish guards; (2) build capacity among fish guards to manage their fishing resources; (3) increase the contribution of fishery communities towards joint patrolling and law enforcement along transboundary rivers by training fish guards in law enforcement and anti-poaching operations and (4) work together with the Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources (MFMR), Ministry of Environment and Tourism (MET - responsible for wildlife crime), the Natural Resource Protection Unit of the Namibian Police (NAMPOL).
Component Two: Exchanging information, learning from other countries, and developing best practices can be an important factor contributing to sustainable development, environmental protection, and climate change adaptation. Namibia is well known for its conservation efforts that resulted in increasing wildlife numbers. However, it is also important to highlight the challenges the country is facing. At the same time, the rewards for illegal behavior are hard to counter using monetary means but the value of pride and dignity can overcome these challenges.
Objective Two: Building community pride for wildlife. Creating a documentary:
The main objective of the documentary is to document Namibian conservation success stories by Namibians, about Namibians, and for a Namibian audience. The documentary will follow communities and custodians of the Namibian environment and look at success stories as well as actions taken to combat wildlife crime. This is about communicating stories to have an impact.
NAMIBIA RHINO
Rhino conservation activities in Namibia
Funding: WWF, Protect African Rhinos
Parnter: MET
Dates: 01/04/2017 - 30/09/2018
Summary
The project aimed at supporting the Ministry of Environment and Tourism in securing and managing funds, targeted toward rhino conservation.
Namibia has experienced a sharp increase in rhino poaching since 2014, and due to this increase in rhino poaching, MET embarked on a dehorning campaign in August 2014, whereby all major rhino populations are being dehorned biannually.
In conjunction with dehorning, all rhinos were notched, microchipped and DNA profiled. In addition, there was also an urgent need to translocate rhinos between populations, out of high-risk areas, and focused on establishing new populations.
Project activities included:
- Rhino dehorning
- Rhino translocations
- Rhino block count
Community Based Natural Resource Management (CBNRM)
Income generation through sustainable Devil’s Claw harvesting project in two Omaheke Conservancies
Title: Income generation through sustainable Devil’s Claw harvesting project in two Omaheke Conservancies
Partners: Social Security Commission (SSC), First National Bank (FNB)
Starting date: 2019-2022
Contact Person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- Train members of conservancies on sustainable Devils Claw harvesting
- Facilitate the creation of 100 seasonal jobs for Devils Claw harvesting
- Facilitate the creation of two permanent employments as focal persons to serve as Buying Point Managers
- Facilitate product development, quality control, and access to markets for Devils Claw
- Contribute to more sustainable management of Devils Claw for long-term benefits
Support to implementation of the COVID 19 related mitigation measures to NACSO Secretariat, working groups and field-based NGOs
Title: Support to implementation of the COVID 19 related mitigation measures to NACSO Secretariat, working groups, and field-based NGOs
Partners:
Starting date: 2020-2022
Contact Person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- Support NACSO Secretariat
- Support NACSO working groups
- Support field-based NGOs
Strengthening CBNRM in Namibia
Title: Strengthening CBNRM in Namibia
Partners:
Starting date: 2020-2023
Contact Person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- Strengthen NACSO as an Association
- Improve government relations and advocacy
- Effective information sharing and communications
Improving governance of the national Community-Based Natural Resource Management (CBNRM) programme
Title: Improving governance of the national Community-Based Natural Resource Management (CBNRM) programme
Partners:
Starting date: 2020-2023
Contact Person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- Develop a good governance culture in conservancies
- Identify change agents/champions to drive good governance and the sustainable CBNRM agenda
- Monitoring impact and engaging adaptive management
Climate Change and Inclusive Use of Natural Resources
Title: Climate Change and Inclusive Use of Natural Resources
Partners:
Starting date: 2021-2022
Contact Person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- Support strategic review of CBNRM programme
- Advice on coordination and support of CBNRM forum
- Advisory inputs to the support facility for niche innovations
- Finalization of Atlas of Namibia
Support to the Kavango Zambezi Transboundary Conservation Area for Sustainable Wildlife Management
Title: Support to the Kavango Zambezi Transboundary Conservation Area for Sustainable Wildlife Management
Partners:
Starting date: 2022-2023
Contact Person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- Development of management and zonation plans – setting up of Salambala fisheries reserve
- Implementation of management and zonation plans
- Adaptive management support
- Management of critical wildlife corridors in KAZA
- NRM trainings for game guards
Leveraging conservation funds for high-value and endangered species
Title: Leveraging conservation funds for high-value and endangered species
Starting date: 2021-2022
Contact Person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- Bankable Wildlife Credit Schemes/Products
- Wildlife Credit agreements signed and operational
- Committees and members aware of their Wildlife Credit programme
Implementation Support Organization Cluster Coordinators Consultancy – for Poverty Oriented Support to Community Conservation in Namibia project
Title: Implementation Support Organization Cluster Coordinators Consultancy – for Poverty Oriented Support to Community Conservation in Namibia project
Starting date: 2021-2023
Contact Person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- Facilitate planning and implementation measures set out by the contractor
- Support actual implementation of approved proposals
- Facilitate implementation of HWC management plans and monitoring
- Report progress
Development of Human-Wildlife Conflict Management Action Plans (HWCMAPs) for identified communal conservancies in Namibia for the Kunene South Landscape
Title: Development of Human-Wildlife Conflict Management Action Plans (HWCMAPs) for identified communal conservancies in Namibia for the Kunene South Landscape
Starting date: 2022
Contact Person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- Development of HWCMAP for Khaudum Landscape and Maurus Nekaro Conservancy
- Development of HWCMAP for Kunene South Landscape, Torra and #Khoadi //Hoas Conservancy
- Development of SVF/Otjozondjupa Landscape, Ondjou, Okamatapati, Ozonahi, African Wild Dog, Otjituuo conservancies
Completed Projects
Omaheke Conservancies
Funding: European Union through the Civil Society Foundation of Namibia
Dates: May 2014 to April 2015
The project was developed in association with three conservancies Eiseb, Otjombinde and Omuramba Ua Mbinda who have received very limited support for the development of their communities. The overall objective is to support rural development in the conservancies by providing critical institutional and governance training, mentoring and technical support in Community-based Natural Resource Management (CBNRM).
Specifically, the project aims to build the knowledge, capacity, and awareness of the communal conservancy members in the areas of governance and organizational management, and to carry out a Sustainable Natural Resource Enterprise Assessment to identify and recommend appropriate income and employment generating opportunities for the conservancy and its members.
The highly successful CBNRM programme has shown that the long-term ability of conservancies to function sustainably is largely dependent upon their ability to effectively govern and manage their organizational responsibilities in a transparent and accountable manner. To complement this training and technical assistance NNF, in collaboration with experts and the community, will identify the most appropriate natural resource-based sustainable development opportunities for that specific community. This will cover areas such as Wildlife, Indigenous Natural Projects, Conservation Agriculture, Rangeland Management, etc., and take into account environmental sustainability and gender and vulnerable population empowerment.
NACSO CLP
Funding: WWF, Hamer Foundation
Partners: WWF Namibia, NACSO
Starting date: 2018
Title: CBNRM Conservation Leadership (CLP) Programme
Contact person: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Location: Field-based, Kavango East, Kavango West, southern Kunene and Erongo regions
The CBNRM Leadership Programme (CLP) was introduced in January 2012 with the goal to develop a cadre of people with the capacity to become future CBNRM leaders. The CLP and the interns require constant management, support, and coordination which have been managed by the NACSO Secretariat (Maxi Louis) in the past. In early 2018, it was decided by the Secretariat and the Board to move these responsibilities to the NNF and to identify and appoint an individual to coordinate the programme.
Overall objective: The CBNRM Leadership Programme (CLP) was introduced in 2012, and in early 2018 the responsibilities were moved to the NNF. The programme provides a mix of training and development activities for four young graduates from higher learning institutions, who undergo a two-year internship with NACSO. It is a blended learning approach matched to the specific needs of the candidates. The different components create a holistic methodology that covers professional/technical and personal development needs that are appropriate for growing the future leaders of CBNRM.
Main Activities:
- Tailored workshops will be offered by members of the cadre and other higher potential candidates working in NACSO partner organizations.
- Capitalize on the frequent invitations for CBNRM personnel to participate in workshops, short courses, and conferences in Namibia and/or the SADC Region. If funding is available interns can also attend workshops and training on an international level.
- During the introduction phase, each intern is assigned to a mentor who they meet weekly and later monthly. In the second year, there could be a rotation of mentors.
- The mentor will be required to assign suitable projects/assignments across the NACSO partner organizations that address development needs. The tasks will be allocated by the programme coordinator.
- Interns will rotate and thus be exposed to key functions within CBNRM. This is not restricted to NACSO and can include partner organizations, MET, or private enterprises.
- Creation of a CLP Alumni Body with an annual get-together.
Namparks III
Funding: German Cooperation (GIZ), financed through KFW
Partners: MET, NNF, GFA
Contact person: MET or NNF Office
Summary:
The four national parks in north-eastern Namibia (Khaudum, Bwabwata, Mudumu and Nkasa Rupara) are at the heart of the Kavango-Zambezi (KAZA) Transfrontier Conservation Area. KAZA is considered the biggest conservation area in the world with a total area of 520 000, square kilometres, with natural attractions and tourism potential.The five neighbouring countries (Angola, Botswana, Namibia, Zambia and Zimbabwe) developed the KAZA for the benefit of the whole region; With Namibia playing a major role in the KAZA, and being at the heart of KAZA, allowing the free movement of wildlife between Botswana and Angola.
The NamParks Project was initiated in 1995 by the Ministry of Environment and Tourism to encourage both nature conservation and socio-economic development in the Kavango and Zambezi (KAZA) Regions. The project is jointly funded by MET and on behalf of the German Federal Government, the German Development Bank KfW provides financial support.The consulting contract commenced in 2014 between MET and GFA Consulting Group GmbH in association with Consulting Services Africa (CSA) and NNF to provide consulting services for the Financial Cooperation Programme “North-Eastern Parks Programme” targeting Khaudum and Nkasa Lupala National Parks. The NNF’s responsibility was to provide technical backstopping to the project through the provision of direct technical staff.
The overall objective of NamParks is to effectively protect the parks against pressures on natural resources, provide a corridor for animal migration and represent a competitive destination for tourists, and to provide residents and neighbours of the parks to profit economically from them.
The main results of NamParks Project are:
- The infrastructure of the North Eastern Parks is improved, such as the rehabilitation of water points in Khaudum National Park and signposting and track maintenance in the parks
- Park management of North Eastern Parks is improved, by establishing monitoring and evaluation tools to assess the conditions of the parks
- Communities benefit from paks and sustainable use of natural resources by supporting Community-based Tourism Enterprise (CBTE)
- MET is supported in its role in KAZA TFCA, and in the development of tourism through collaboration with the Namibian Tourism Board and professional associations for the promotion of tourism in the region
- Ensure the MET Project Management team is supported and advice on strategic and technical planning and project implementation
The Nkasa Lupala and Khaudum National Parks infrastructure were inaugurated in September 2017 and November 2017 respectively.
CBNRM Omaheke Support
Funding: Social Security Development Fund, US Embassy, FirstRand Foundation
Starting date: October 2018 - June 2021
Title: Income generation through sustainable Devil’s Claw harvesting in 3 Omaheke conservancies
Contact person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Location: Omuramba ua Mbinda, Eiseb and Otjombinde
Project background
The conservancies of Eiseb, Omuramba ua Mbinda, and Otjombinde were gazetted between 2009 and 2011 and apart from efforts by the Namibia Nature Foundation in 2014 & 2015 and now more recently in 2018; these areas have received little support. Currently, the Namibia Nature Foundation is supporting the conservancies with Devils Claw harvesting.
The overall goal of this intervention is to strengthen conservancy management structures and their ability to manage natural resources, in line with the CBNRM programme and to support better delivery of the Devils Claw harvesting project, whereby managers assist with quality control and buying point coordination and game guards support resource monitoring activities. The specific objectives are
- To capacitate and empower conservancies to fully explore income-generating practices
- To capacitate and empower conservancy managers to work with their committees and the Ministry of Environment and Tourism for better management outcomes.
- To capacitate and empower conservancy game guards to work with their managers, committees, and the Ministry of Environment and Tourism for improved wildlife management
- Improve wildlife management with an emphasis on mitigating human-wildlife and combatting wildlife crime.
- To support conservancy members in deriving income from available resources to supplement cash flows
Hunting for Opportunities: Promoting Business and Employment for Communal Conservancies
Funding: Funded by the Finnish Embassy in Namibia, through the Fund for Local Cooperation
Project Date: September 2014 - December 2016
Namibia is a country blessed with incredible landscapes, wildlife, and people making it an increasingly attractive tourism destination. It is also home to one of the world’s most progressive and successful conservation initiatives the Community Based Natural Resource Management Programme. This programme has, in the last 20 years seen almost half of all communal land areas and 20% of Namibia being designated as conservancies by the people themselves. Hunting tourism is particularly vulnerable to the trophy hunting market and this project developed alternative non-trophy hunting systems that directly support the management objectives of conservancies. The conservancies have three types of quota available to them, a trophy quota, a shoot and sell quota (meat), and an own use quota.
The management of the shoot and sell quota and own use quota was improved to better align them with management objectives, to become more efficient, and also to raise more income and enhance the value of wildlife. The Finnish Embassy in Namibia through its Fund for Local Cooperation has provided funding to the Namibia Nature Foundation to look at ways of promoting non-trophy hunting specifically to the Finnish market, whilst at the same time promoting business opportunities. The project aimed to pilot two types of hunting which are non-trophy and target a group hunting experience;
- Professional Package: this package is run by a professional outfitter Esterux Safaris and targeted towards groups (4 persons) wanting a more professional experience and should be particularly interesting for the business market, either those wishing to explore business opportunities in Namibia or targeted corporate events, particularly for those in the hunting industry (weapons, ammunition, optics & clothing companies). The package involves hunting a set quota of animals for utilization by the community and depending on the clients can involve more or less community engagement, e.g. being involved in the meat handling and distribution to households or not.
- Conservancy Package: This package is intended to be more of a self-drive safari, aimed at groups (4 persons) of hunting friends or for targeted corporate team building. The emphasis is on hunters being self-sufficient in terms of transport and food and being hosted in a conservancy, where local guides will facilitate the hunting. The hunters will be directly involved in the daily planning and execution of their hunting together with their hosts and will assist with the post-hunt processes, meat handling, and distribution or processing. This is designed to be a very immersive and personal experience.
The target areas are Conservancies in Erongo and Kunene to date we are working with Orupembe and Sanitatis and are exploring options in Erongo. This project was carried out in consultation with the Ministry of Environment and Tourism and in close collaboration with NACSO, NAPHA and the Finnish Hunters Association, and Estreux Safaris.
Links:
http://www.napha-namibia.com/home/
http://www.nacso.org.na/index.php
PROBATS Brandberg GeoPark- Consultancy
Funding: Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Partners: Ministry of Industrialisation, Trade and SME Development
Title: PROBATS Brandberg GeoPark Facilitation
Contact person: Nabot Mbeeli This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Project Background
The Promotion of Business and Transformational Services (hereafter referred to as ProBATs) is jointly carried out by the Ministry of Industrialisation, Trade and SME Development (MITSMED) and the Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ). The objective of ProBATs is to enhance the conditions for entrepreneurial activity in Namibia, which should allow Namibian businesses to realize their growth potential.
The programme includes both the implementation of Industry Growth Strategies (IGS) in six to seven sectors and the enhancement of Business Development Services (BDS) for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). The IGS identifies constraints and opportunities pertaining to input supply, production technologies, marketing and trade, service provision, and framework conditions. They further propose specific interventions and projects to strengthen the industries. Implementation of the IGS not only needs the commitment of the relevant stakeholders in the respective industries but also workable structures and procedures.
Objectives:
- Creation of a regular income and thus essential improvement of the living conditions of small miners in the region.
- Improving market access and thus the possibility to sell minerals and locally produced jewelry
- Opportunity for tourists to discover/mine their own gems under the guidance of small miners, with appropriate basic equipment.
The achievement of these objectives will mark a first step towards the eventual development of a Geopark centered on the Brandberg area.
GIZ-CBNRM Project
Funding: Deutsche Gesellschaftfur Internationale Zusammerbeit (GIZ)
Partners: WWF, NACSO
Starting date: 2017
Title: GIZ - Community-based Natural Resource Management Conservancy Support
Contact person: Aina Andreas (Kavango) This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. or This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. (southern Kunene, Erongo)
Location: Field-based, Kavango East, Kavango West, southern Kunene and Erongo regions
Project background
The main objective of this project is to strengthen NNF support activities for CBNRM. Specifically, the project focuses on consolidating the support to conservancies in the areas where NNF is already active by supporting the Ministry of Environment and Tourism (MET), the conservancies, and the community forests to be compliant with CBNRM, to ensure a process of value chain development, which will allow an income increase for communities as well as strengthening their resilience to the effects of climate change through climate change adaptation.
Within three components, the project centralizes support for finance management, backstopping support, exchange meetings, logistics, and office support, as well as providing crosscutting technical support. The components are:
-Support to existing and emerging conservancies in Kavango East and West regions
-Support to conservancies in southern Kunene and Erongo regions
-Resolving human-wildlife conflicts (HWC) in Kunene south and Erongo regions
Project outcomes:
The main outcomes of the activities under the components are to create an enabling environment for new developments in conservancies to increase resilience and for improving the livelihood of conservancy members in Kavango East, West, southern Kunene, and Erongo.
In summary, the project aims to achieve the following:
- Conservancies can increasingly comply with the Namibian legislation related to CBNRM
- Conservancies are relevantly equipped and trained to sustainably and efficiently manage their finances
- Conservancies are relevantly equipped and trained to sustainably manage their natural resources
- The livelihoods of conservancy members have improved through consolidated or newly established opportunities
- The resilience to negative effects like HWC, climate change, or wildlife crime has increased
- Conservancies are able to develop and implement appropriate HWC prevention measures
- Conservancies are able to develop and submit adequate reports to their members and the ministry, and therefore increasingly comply with the legislation and good governance requirements and;
- Conservancies are able to access funds for rural development and climate change adaptation
Support to the establishment and maintenance of sustainable financing schemes for communal conservancies in southern Kunene and Erongo regions, Namibia
Partners: WWF, NACSO
Starting date: 2015
Title: Support to the establishment and maintenance of sustainable financing schemes for communal conservancies in southern Kunene and Erongo regions, Namibia
Contact person: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Funding: Funding for this grant is provided by WWF Netherlands through the WWF Namibia office
Location: Field-based, southern Kunene and Erongo regions. Coordinated from regional NNF office in Walvis Bay, Erongo
Project Background
Tourism ventures contribute to livelihoods in the region where they operate in multiple ways, including direct contractual cash payments to conservancies, salaries for employees, staff training, and related benefits such as payments of cash and in-kind contributions (equipment, donated services, etc.) to village development committees, local schools, etc.
On the other hand, many species (elephant, lion, leopard and hyena) create major problems for local residents, by killing livestock, damaging infrastructure and attacking people. While there is generally a net benefit in terms of the overall benefits generated by these species, individual farmers and community members bear a disproportionate share of the costs associated with HWC. Further, the benefits that are generated are not clearly linked to the presence of those species causing the problems.
It is obvious that whilst CBNRM has been generating significant and extremely impressive benefits through tourism and other activities, the average community member simply is not seeing the connection between the presence of these problem-causing species and a successful tourism operation. It is critical that species-focused payment mechanisms be established so that these, often rare and endangered species can begin to acquire a tangible tourism value.
This project builds on the support that NNF has provided to conservancies in Kunene south and Erongo by helping to identify and establish such payment schemes. The payment schemes and associated actions are:
- Focused on creating awareness around HWC in conservancies for tourists visiting lodges
- Setting up a transparent and effective payment mechanism that will allow tourists and lodge operators to make a voluntary donation towards the mitigation of damage caused by wild animals such as elephant
- ‘ring-fencing’ these funds to be used exclusively for HWC compensation or other mitigation measures such as HWC research and helping to ensure that the mitigation measures are identified in a participatory manner, making sure to take the needs of local farmers into account
- Sourcing match-funding for donations so that the amount for compensation is doubled or more by the time it reaches affected farmers
This is an ongoing project and is linked closely with other initiatives both in the conservancies in which we work but also on a national level.
Thatch Grass Value Chain
Funding: GIZ in (June – December 2016)
The Namibia Nature Foundation was contracted to assess the existing thatch grass value chain and how communities may increase the benefits that are generated from it in the areas of Muduva Nyangana, George Mukoya Conservancy, Community Forest, and Katope Community Forest. Local people in the Kavango regions have generally few livelihood options and little access to transport, services and formal employment. It is estimated that the Kavango regions have the potential to produce over 1 million bundles of 60cm circumference thatch grass annually. However little of this potential is realized for the benefit of local people: The cutters in the communities often barter for products (i.e. groceries, school supplies, etc.) at a very cheap “exchange rate”, instead of getting cash. The value they sold the grass for was approximately N$5 for a 60 cm bundle in 2014. The primary traders then provide treatment to the grass before selling it to secondary traders - mainly the construction industry – for N$20 for a 60cm bundle. Secondary traders, who ultimately provide the product to the end user, receive anywhere from N$64 to N$140 for a 60cm bundle.
With thatch grass, most value is added by transporting the goods to market and by using labor to process it into the final product which can add another 50-350% value. The 2014 price of N$5 for a 60 cm bundle eventually caused community members to stop selling grass to primary traders. Local people did not believe that the price reflected fair compensation for their work. This, together with some other factors including Foot-and-Mouth disease (limiting the trade) has caused the thatch grass market to break down. As a result, many end users shifted to substitute products like canvas roofs or South African grass.
The end users tend to be individuals who use thatch grass roofing material, often in upmarket lodges or private houses within Namibia but also abroad. In 2014, the main destination of thatch grass was Angola (60%), however by 2016 this had declined to 5%, likely due to the country’s economic decline. In the same period, the amount of thatch grass going to North-Central Namibia increased from 15% to 50%, which is believed to be attributed to the region being under development. In order to develop a value chain for thatch grass moving forward, it is recommended that the mandate over thatch grass is clarified and that a well-structured value chain with clear value-addition with as few middlemen as possible be established. It is also recommended that there are controls to ensure quality and sustainable harvesting and to tender a concession for thatch grass to a professional firm.
Education and Lifestyle
Expansion of the University of Namibia (UNAM), Extension of the Katima Campus (Component 2)- NNF Consultancy
Funding: German Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (KfW)
Partners: University of Namibia (UNAM)
Starting date: 2016 - 2024
Title: Expansion of the University of Namibia (UNAM), Extension of the Katima Campus (Component 2)
Contact person: Mirja Stoldt This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Project Background
Earlier estimates show that currently, about 900 positions in conservation at higher management levels in public and private institutions and the private sector with or corresponding to a Namibian National Qualification Level of 8 - 10 (bachelor’s degree to Ph.D.) are not filled in the SADC region with sufficiently qualified staff. In Namibia, about 500 qualified employees are needed in the conservation sector. Therefore, the University of Namibia (UNAM) has established a Department of Wildlife Management and Ecotourism (DWME) at the University of Namibia in the Katima Mulilo Campus under the Faculty of Agriculture and Natural Resources (FANR).
The Faculty of Agriculture and Natural Resources (FANR) has been in existence since 1996. The Faculty’s mission is “to promote sustainable agricultural and natural resource development and management in Namibia, through teaching, research, and extension services to communal and commercial farming communities”. The University of Namibia (UNAM) has established the new Department for Wildlife Management and Ecotourism (DWME) as part of the Faculty for Agriculture and Natural Resources (FANR) in Katima Mulilo, planning on adding research possibilities and possibly developing an Institute/Faculty for academic education in the field of protection, conservation and the use of natural resources with five new departments and special reference to wildlife management in the Zambezi Region.
From 2016 through 2024, German Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (KfW) is supporting UNAM in further developing the Katima Mulilo Campus. The Project concerns the enlargement of the Department of Wildlife Management and Ecotourism (DWME) at the University of Namibia (UNAM) Campus Katima Mulilo under the Faculty of Agriculture and Natural Resources (FANR). The purpose of the Project is to improve the management of natural resources and the infrastructure of protected areas in the Southern African Development Community (SADC) region.
In order to achieve the goals, an extension of the existing campus, appointed to a new plot, will be built. In addition, applied training courses will be developed, the existing curricula revised, training and research activities will be created and networks with a variety of stakeholders will be established. The DWME trains experts in Wildlife Management and Ecotourism, urgently needed in the SADC region at Bachelor's and Master's levels to stimulate state of art research activities. This will help to better protect and conserve Trans-Frontier Conservation Areas (TFCA), use natural resources sustainably, and develop the area into a competitive tourist destination. The Project will, therefore, contribute to the economic development of the region and supports its integration.
The KfW supported and BMZ financed programme to extend the Katima Mulilo Campus of UNAM allowing UNAM to exemplify an image and ideal of excellence in the field of Wildlife Management and Ecotourism education and research sector. The programme and respective educational extension would act as a beacon to the countries of the Southern African Development Community (SADC) regarding transboundary management of natural resources and the structures of protected areas in the SADC region.
The programme consists of two components:
- Component 1: Architectural Design / Engineering / Infrastructure,
- Component 2: Teaching / Training / Research.
The aim of Component 2, for which the Namibia Nature Foundation (NNF) is a consultant, is to develop innovative, practical-oriented, and integrated training courses suitable for the target group described. In detail, it is planned – amongst others - to adapt the existing BSc (Hons) and develop a new MSc by coursework curriculum. This means that new teaching modules and methods must be developed, with the participation of the private sector. Also, the qualifications need to be accredited to be recognized by the neighboring countries. It is intended to involve national, regional, and international experts and stakeholders in this process, e.g. through summer schools or workshops, individual contacts, or scientific exchange.
Completed Projects
Updating Information and Data on Geographic, Environmental and Socio-Economic Features and Statistics of Namibia - NNF Consultancy
Funding: Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Partners: Research and Information Services of Namibia (RAISON)
Starting date: Nov 2018 - April 2020
Title: Updating Information and Data on Geographic, Environmental and Socio-Economic Features and Statistics of Namibia
Contact person: Mirja Stoldt This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Project Background
A comprehensive atlas about Namibia’s geography was published in 2002. The book was subsequently reprinted several times in response to demand from the public and educational institutions. The last edition was printed in 2010. However, all the reprints relied on the original data sets predating the original 2002 publication.
As the country continues to develop – especially in sectors that require enhanced education, knowledge, and awareness – up-to-date and reliable information on the country’s physical, human and natural environment is a necessity. This is further supported by the persistent requests to the authors for a new edition and/or new data.
Therefore, the time has come to compile and publish a new Atlas of Namibia. This will meet the existing demands of the old atlas and provide an opportunity to present new and updated information about Namibia. A variety of information will be analyzed and presented to demonstrate and assess changes in Namibia during the past three decades.
The Atlas will be the authoritative reference on Namibia’s geography for decision-makers, resource managers, researchers, and students. It will be a vital tool for education and training. Furthermore, the information in the Atlas will be used to promote Namibia and its economic growth.
Objective
“To update information and data on the geographical, environmental and socio-economic features and statistics of Namibia.”
The goal is to produce…
- A thoroughly researched, well-coordinated high-quality information and data source, which is presented and distributed to key stakeholders in electronic form.
- A state-of-the-art source of information and data on environmental, ecological, and socio-economic indicators, which is visualized and presented in high-quality maps, diagrams, and up-to-date imagery.
- Useful information and data resources that serve as a reference for key environmental planning and reporting processes e.g. within the SGD, NDC, Rio Conventions, NDP reporting, the proposed Integrated State of Environment Report, and the State of Environment Conference.
Namib Desert Environmental Education Trust (NaDEET)
Project: Co-sponsorship of Schools for Environmental Education at NaDEET Centre
Start and end date: January 2015 - December 2017
Contact person: Viktoria Keding This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
The Nedbank Go Green Fund supported the NaDEET Centre since its inception in 2002. This lasting relationship has been significant in the success of NaDEET for the past years to reach its goals and provide ongoing excellent service delivery of environmental education.
The project supported environmental education at NaDEET Centre for school's
The project's objectives were:
- To financially support learners and schools that have made NaDEET Centre a part of their annual school calendar.
- To support conservation through environmental education for schools
- To protect the natural environment through improved access to environmental education and thereby increased knowledge, understanding, and awareness of environmental problems, and solutions.
Visit the NaDEET website here
Natural Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Forestry
Zambezi State Forest Area Support
Title: Zambezi State Forest Area Support
Funding: European Union (EU)
Date: 2021-2022
Contact person: Frances Chase fchase@This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objectives:
- To strengthen land management through improved land use planning,
- Reduction of environmental degradation
- Consideration of ecological service provision, and Improved livelihoods
Introduce Mechanisms to Restore Degraded components of the ZSFA
Title: BEEKEEPING IN THE ZAMBEZI: A FEASIBILITY STUDY
Funding: COmON Foundation
Date: 2022 – 2023
Contact person: Frances Chase fchase@This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.

Objective:
- Engaging with communities adjacent to ZSFA to develop CF
- Developing detailed funding proposals for community forest projects, and fundraising
- Promoting “Herding for Health” approach within the State and community forests as a means of increasing the community benefits from the State Forest
- Undertake a full biodiversity inventory
- Develop funding proposals for implementation of species plans and sustainable use of valuable species
- Support and capacity to MEFT / Directorate of Forestry with the implementation of Zambezi State Forest management plan
African Botanical Resource Innovation and Value Addition in KAZA
Title: African Botanical Resource Innovation and Value Addition in KAZA
Funding: GIZ
Date: 2021 – 2022
Contact person: Frances Chase fchase@This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objectives:
- Identify and commercially develop new botanical ingredients from the KAZA region;
- Build ABS-compliant, sustainable supply chains for these ingredients from local communities; and
- Develop local-level value addition opportunities where possible.
Implementing an integrated approach to Natural Resource Management in the Middle Cubango-Okavango Basin to mitigate land degradation
Title: Implementing an integrated approach to Natural Resource Management in the Middle Cubango-Okavango Basin to mitigate land degradation
Funding: European Union (EU)
Date: 2021 – 2022
Contact person: Frances Chase fchase@This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objectives:
- Reduced risks of riverine degradation through integrated Natural Resource Management;
- ObjectivReduced vulnerability of communities through diversification of income streams opportunities and food sources;
- Increased knowledge of policies around degradation and biodiversity loss.
Completed Projects
Man and Biosphere - Consultancy
Funding: UNESCO
Dates: August 2012 – August 2013
UNESCO Man and Biosphere (MAB) Reserve Feasibility Study
NNF carried out a feasibility study on the possible creation of a UNESCO Man and Biosphere (MAB) reserve in Namibia. MAB, an international programme established in 1971 with over 500 reserves in 117 countries. MAB reserves comprise three main functions: conservation, development, and logistic support. MAB in Namibia focused on Mudumu North complex in East Caprivi which includes four conservancies (Mashi, Muyuni, Sobbe, and Kwando), two protected areas (Bwabwata and Mudumu national parks), and commercial enterprises such as lodges.
The aim of the project was to quantify and qualify the potential impacts of a Biosphere Reserve in Namibia.
Main activities:
- review of other MAB reserves in Southern Africa
- collection of field data from the Caprivi region
- where appropriate, cost-benefit analysis
The MAB programme combines science, economics, and education to improve human livelihoods and safeguard ecosystems, as well as providing research and logistical support to areas that are significant for biodiversity conservation. MAB status helps to raise the profile of an area, enables knowledge sharing with the MAB network, and can help to leverage funding.
Succulent Karoo Ecosystem
Overview
This programme was part of a global initiative in support of conservation and sustainable development in biodiversity hotspots around the world. Namibia's hotspot is the Succulent Karoo which spans western parts of South Africa and southern Namibia.
In Namibia the programme was run by the Namibia Nature Foundation (NNF). Nearly US$ 1 million was allocated by the Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund to the Namibia component of the Succulent Karoo Ecosystem Programme (SKEP) in support of conservation and sustainable development activities in the Succulent Karoo. Namibia's priority area is the Sperrgebiet.
Aim of SKEP Namibia
"Biodiversity in the Succulent Karoo Ecosystem of Namibia is effectively conserved and managed by the state and civil society through an integrated programme of conservation action and co-management for the sustainable development of the region, the national economy and the livelihoods of people."
NNF's involvement with the programme began in 2004 and included programme management and implementation; coordination within Succulent Karoo Ecosystem and buffer areas; secretariat services to the steering committee; networking, facilitation and coordination with parallel projects; small grants management; financial management; monitoring and evaluation. The final NNF project as part of the SKEP programme, completed in 2012, was providing strategic support to the consolidation of the management and development of the newly proclaimed Sperrgebiet National Park and immediately adjacent areas.
Terrestrial Species Research
Mountain Zebra Project
Title: Mountain Zebra Project
Funding: Rufford Foundation, Parc Zoologique de Montpellier, Gaia Nature Fund.
Partners: Namibia Nature Foundation, Ministry of Environment and Tourism (MET), Gondwana Canyon Park, Ai-Ais/Fish River National Park, NamibRand Nature Reserve, Büllsport Guest Farm, Namib-Naukluft National Park, Gondwana Namib Park, Solitaire Land Trust, Pieter Henning Foundation, Hobatere Tourist Concession and Etosha National Park, University of Newcastle.
Date: 2005 - ongoing
Contact person: Professor Morris Gosling (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.)
About Project:
The Mountain Zebra Project is co-ordinated by Professor Morris Gosling of the University of Newcastle, UK, in partnership with landowners and conservationists who share the aims of mountain zebra conservation, of scientifically based management, and of affection for this tough and charismatic species. The Project started in 2005 in Gondwana Canyon Park and the neighboring/Ai-/Ais National Park and, in order to provide comparative information in areas of different rainfall, has subsequently expanded to NamibRand Nature Reserve, the Namib-Naukluft National Park, the Gondwana Namib Park, Büllsport Guest Farm, the Solitaire Land Trust, the Hobatere Tourist Concession area and Etosha National Park. Hartmann’s mountain zebra (Equus zebra hartmannae) is Namibia’s only large mammal endemic (except for small numbers in southern Angola and northern RSA) and is a Specially Protected Species in Namibia. It is a subspecies of mountain zebra and together with the Cape mountain zebra (E.z.zebra) in South Africa is of global conservation importance (IUCN Red List Category: Vulnerable). While Hartmann’s populations in Namibia are healthier and more widespread than Cape mountain zebra, they are vulnerable to severe droughts, particularly where fences prevent movement to scarce grazing.
Main Aim:
The aim of the Mountain Zebra Project is to promote the study of mountain zebras for scientifically based population management and as a flagship species for wider ecosystem conservation in Namibia. Like many large mammals in human-dominated landscapes, mountain zebras have a complex relationship with people. They are a threatened sub-species and in places suffer from unsustainable exploitation, but they can also become locally abundant and cause overgrazing, particularly in the arid, fragile habitats that are typical of most of their range in Namibia and where their natural predators have been reduced or eliminated. In addition to their significance as an iconic member of Africa’s equids and deserving of conservation in their own right, they are also an economic resource of great value when properly managed. They represent a subtle variation on the equid theme and their biology, including the population processes that underpin variation in abundance contains many unsolved problems.
Zebra stripe patterns, like human fingerprints, are individually distinct, and once photographed in a standardized way, animals can be followed throughout life. This allows an individual-based approach, a suite of techniques now widely used in behavioral and population biology, and provides the basis for quantifying such key processes as age-dependent survivorship which is needed to understand and model population dynamics. Mountain zebra are water-dependent and camera traps set at waterholes are being used to monitor entire populations and their movements, even those in inaccessible mountainous areas such as the Naukluft extension of the Namib-Naukluft NP, a mountainous area that was designated for mountain zebra conservation.

Vultures Namibia
Funding: Donations from Namibian businesses and individuals, fund-raising dinners in Windhoek and Swakopmund.
Contact persons: Peter Bridgeford This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it., Holger Kolberg This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it., Mark Boorman This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Introduction to the Vultures Namibia projects
In Namibia, five species are found and one is extinct.
| White-backed Vultures | Hooded Vultures |
| Lappet-faced Vultures | Cape Vulture |
| White-headed Vultures | Egyptian Vulture (extinct as a breeding species) |
Human activities have had a severe impact on vultures all over the world through:
- Habitat destruction and degradation.
- Poisoning
- Electrocution
- Drowning in farm reservoirs.
- Disturbance at colonies.
- Direct persecution by means of shooting and gin trapping.
- Illegal collection of birds, bird parts and eggs for traditional medicine and trade.
Vultures are primarily scavengers. They not only prevent the spread of disease from dead animals but also provide the farming community with a service by disposing of livestock carcasses. The alternative is to burn or bury the carcass, both time-consuming and expensive. Vultures in the sky draw the farmer's attention to dead animals on his farm, often domestic stock, an important factor on the huge properties in Namibia. It is thus important to ensure that existing vulture populations are able to continue to survive, despite the pressure of human activities.
Aims and Objectives of the Project
Promote vulture conservation amongst the farming and rural communities of Namibia.
- Assess the population status of Namibian vultures through monitoring of breeding populations.
- Resolve any human/vulture conflicts on an ongoing basis.
- Maintain the awareness and education campaign amongst the public in Namibia.
Details of the projects
Namib-Naukluft Park
Vulture populations cannot be censused in the way of plain's game or other large animals. However, by censusing breeding birds and comparing the annual breeding rate in an area, the health of a population can be determined without counting the total population. This project in the Namib-Naukluft Park started in 1991. Vultures Namibia has been doing annual aerial surveys to find the nests of breeding Lappet-faced Vultures since 2001.
On commercial farms
The project on commercial farms involves the farmer, his family and workers and brings the plight of vultures to the notice of these people. This project has been very successful because it involves the people living on the land and is a ‘hands-on’ project.
Vultures Namibia is a non-profit organization, staffed by volunteers. All funds are used for ringing and monitoring the endangered and threatened vultures and not for salaries or gratuities. All funds are channelled through the Namibia Nature Foundation (NNF) and their accounts are audited annually.
Funds can be deposited directly in the Vultures Namibia account at the NNF:
NNF Sundry Trust
Nedbank Namibia
Main branch 461-617
Account: 11 00 00 49 86 9
Reference: Vultures Namibia
Crane and Raptor Working Groups
Overview
Namibia Nature Foundation (NNF) supports two working groups that focus on the conservation of Namibia's birdlife and its habitats.
Namibia Crane Working Group
This working group was formed in May 2004 as a result of a concern for the continued survival of Namibia's crane species and their habitats. The group has drawn up a Namibia Crane Action Plan and is working to put this plan into action to conserve cranes and their habitats in partnership with the people who share these habitats.
Activities include effective communication, supported by regular newsletters, crane counts, local crane awareness surveys, guide training, and planning of a crane/wetland-based tourist route in the north. Sightings of cranes (including any ring combinations) are welcome: please see the link to the flyer below for details. Note that newsletters No. 1-52 are available on request from email This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Flyers:
Report Your Blue Crane Ring Resightings
Newsletters and Articles:
Namibia Crane News No53, April 2015
Namibia Crane News No54, Nov 2015
Namibia Crane News No55, May 2016
Namibia Crane News No56, Dec 2017
Namibia Crane News No57, Sep 2018
Namibia Crane News No58, July 2019
Namibia Crane News No59, July 2020
"Etosha's Exclusive Blue Cranes" published in the Travel News Namibia Autumn 2018 pg. 73
Raptors Namibia Working Group
Namibia's vultures, other diurnal raptors and owls are increasingly under threat from factors such as disturbance, particularly at breeding sites; the misuse of poisons and pesticides; electrocution and collisions with overhead lines; habitat degradation; persecution; illegal harvesting; and drowning in reservoirs. The Raptors Namibia working group was established in 2005. The group focus on six key priority areas :
- Promote co-ordination and communication with key stakeholders
- Obtain information/data
- Promote awareness and education
- Manage raptor populations and habitats by addressing threats
- Build capacity
- Define protocols and policy and promote the enforcement of legislation
Productive Land and Seascapes
Knowledge Centers For Organic Agriculture - Knowledge Hub Southern Africa (KHSA)
Project Name: Knowledge Centers For Organic Agriculture - Knowledge Hub Southern Africaouthern Africa Knowledge Hub (KHSA)
Funding: Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Partners: Namibia Organic Association (NOA) and Namibia Nature Foundation (NNF)
Starting date: 2019-2022
Target Area: Kavango West and East, and Zambezi Region
Contact Person: Marieke Voigts, Project Coordinator, This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- The actors of the knowledge hubs and their networks in the regions of Eastern and Southern Africa, West, North and Central Africa are strengthened in their role of promoting organic agriculture and agroecology.
- improved access to and dissemination of knowledge (collection, preparation and dissemination)
- Enhance multiplier capacity (strengthening competence)
- Build and/or strengthen networks and relationships including establishing and supporting PGS groups
Food security and habitat protection in KAZA - KAZA ARISE
Project Name: Food security and habitat protection in KAZA – KAZA ARISE
Funding: German Federal Ministry of Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), through the Bengo Engagement Global program, and World Wildlife Fund (WWF)
Partners: Integrated Rural Development and Nature Conservation (IRDNC)
Starting date: 2021-2024
Target Area: Kavango West and East, and Zambezi Region
Contact Person: Marieke Voigts, Project Coordinator, This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Project Summary
This aims to bring stakeholders together to promote agroecological approaches in crop and livestock production. The successful adoption of these approaches should increase food production in smaller areas without shifting cultivation and thus safeguard wildlife habitats and diversify income through the sale of surplus produce. Project activities include crop and vegetable cultivation, livestock production, civil society advocacy, and transboundary collaboration (including Zambia and Zimbabwe).
Objective:
- At least 625 smallholder households in the project area in Namibia benefit from enhanced food security and livelihoods while reducing the degradation of natural habitats and land conversion.
- On a national level, political and institutional support for sustainable agriculture including livestock keeping is enhanced by the active political participation of civil society actors.
InfoRange - Increasing efficiency in rangeland-based livestock value chains through machine learning and digital technologies
Project summary
Pastoral livestock production on rangelands is an important land-use system and contributes between 15 and 60 % to the agricultural GDP of countries in eastern and southern Africa. Largely mobile herds exploit the temporal and spatial heterogeneity in resource availability (pulses) on rangelands. This production strategy has advantageously low fossil fuel input needs but is very knowledge and information intensive. Therefore opportunities derived from digitalisation will have a high potential to increase efficiency (‘precision pastoralism’).
To successfully introduce the technology InfoRange uses a transdisciplinary approach to co-design the ICT solutions with users and embeds them in social innovations. By an actor- and activity oriented approach we build on the knowledge of different involved actor groups to understand how their decision-making can be improved through ICT.
Co-designed ITC solutions will enhance sustainable rangeland use and efficiency in livestock production through improved grazing management and veterinary service provision. InfoRange will combine user-generated information (e.g. similar to geotagging photos in google maps or live traffic updates) with remotely sensed data. State-of-the-art machine learning models will be developed to analyse the generated crowd data (e.g. time series), capture and understand phenomena such as differences in pasture use intensity as well as classify and recognise patterns in different scenarios. Including representatives of different governance bodies from the onset of the project permits to creation of outputs in formats suitable to enhance policy decisions.

- German Institute for Tropical and Subtropical Agriculture– DITSL
- Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering of the University of Kassel (UK)
- Center for Research and Development in Drylands - CRDDCenter for Research and Development in Drylands– CRDD
- University of Nairobi (UoN)
- Namibia Nature Foundation (NNF)
- Namibia University of Science and Technology (NUST)
Objectives
InfoRange aims at improving rangeland use and governance and increasing resource-use and production efficiency in rangeland-based livestock production through digital and ICT applications/services that permit user-generated information acquisition and transmission. It also seeks to contribute to integrating external telemetry and observatory data with land-user generated data on bio-geo-physical ecosystem features in order to render digital and ICT services more relevant for land-users’ immediate management decisions on grazing, watering and health management.
InfoRange uses transdisciplinary approach to
- Adapt, modify and further develop existing ICT tools for decision support in rangeland management and use as well as for veterinary service provision
- Develop procedures and solutions to enhance the use of ICT tools by land-users and increase their distribution and accessibility under reduced network coverage
- Combine approaches from citizen-science, crowd-data sourcing, machine-learning and participatory monitoring and evaluation to render these tools more relevant for decision making at different governance levels
Project location
In Kenya, the project will be implemented in the northern arid and semi-arid Marsabit County in Laisamis and Moyale Subcounties – i.e. two study locations. In Namibia, InfoRange will be implemented in the Kavango East Region (including the Ndiyona Constituency) and Omaheke Region (including the Otjombinde Constituency). The chosen sites represent communal livestock-management systems, which will ensure that the techniques developed for better resource monitoring and evaluation (M&E) are relevant for the people on the ground and will enable an easy scaling-up of the project activities.
Project structure, work packages and their tasks
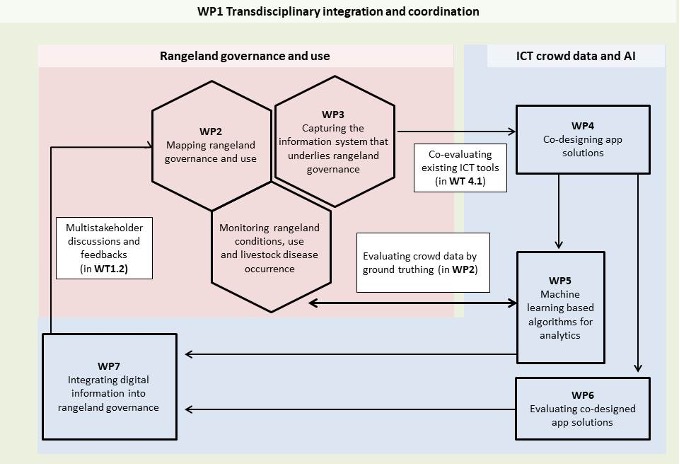
InfoRange is structured in seven Work Packages (WPs) with defined Work Tasks (WTs) for each WP

Marine Species Research and Conservation
NIMPA+

Project Name: Strengthening Namibia's Marine Protected Area management and improving livelihood opportunities of coastal communities
Project Donor: Blue Action Fund (BAF), Oceans 5, Shark Conservation Fund, Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB)
Partners: Namibia Nature Foundation (NNF) as the lead grantee and Blue Marine Foundation (Blue Marine); GRID-Arendal (GRID); TheSouthern African Foundation for the Conservation of Coastal Birds (SANCCOB); South Atlantic Environmental Research Institute (SAERI); Community Skills Development Centre (COSDEC Benguela)
Project period: 2023 - 2027
Objectives:
The project will support the Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resource (MFMR) in employing the following strategies and technical approaches to achieve the four following project objectives:
Objective 1: Update and strengthen the formal management system of NIMPA and the capacities needed to implement it effectively
Objective 2: Engender broad support for NIMPA from civil society and engaged coastal communities
Objective 3: Strengthen and diversify coastal livelihoods
Objective 4: Scale up marine conservation efforts nationally based on the successes of NIMPA
Oceans 5
Project Name: Oceans 5 - Strengthening the effective management of the Namibian Islands Marine Protected Area (NIMPA) and expansion of MPA network in Namibia
Project Donor: Rockefeller Philanthropy Advisors
Partners: Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources and, The Fisheries Observer Agency
Starting date: 1st April 2022 - March 2023
Goal: To strengthen NIMPA and MPA management effectiveness and expand the network of MPAs in Namibia
Objectives:
- Support Management Planning and Implementation of NIMPA
- Supporting increased Marine Protection Areas in Namibia
- Improve Technical Capacity for and Sustainable Financing of Marine Conservation in Namibia
- Increased political support and public knowledge to raise awareness on the importance of marine conservation and the role of MPAs
Namibia's Rays and Sharks
Project Name: Namibia's Rays and Sharks (NaRaS)
Project Donor: Shark Conservation Fund
Partners: South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity (SAIAB), Abalobi, Vericatch, The Fisheries Observer Agency, and the Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources.
Starting date: 2022
Key Activities:
- Collaboration with recreational anglers along Namibia's coastline, to record their catches.
- Recording shark and ray bycatch in commercial fisheries.
- Developing the first comprehensive species list for chondrichthyans in Namibian waters, and a species identification guide.
- Research to better understand the sharks, rays, and chimeras using the Namibian Islands Marine Protected Area and their movements both within and beyond the MPA.
Anticipated Outcome:
Almost no research has been done on chondrichthyans in Namibian waters, but we know that healthy shark, skate, and ray populations are an important part of healthy oceans. This project will establish, for the first time, the chondrichthyan species present inside the NIMPA and in other key marine habitats along Namibia’s coastline, and will inform management strategies for those species. The data generated can also contribute to future decisions around the designation and management of MPAs, to maximize benefits to chondrichthyans.
Albatross Task Force
Project Name: Albatross Task Force - Reducing seabird bycatch in Namibian demersal longline and trawl fisheries
Project Donor: Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB)
Partners: Birds Life Internation and the Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources.
Starting date: 1st April 2022 - March 2023
Goal: To improve compliance with seabird bycatch regulations in the trawl fleet; ensure that demonstrated seabird bycatch reductions in the Namibian longline fishery are sustained over the long-term
Objectives:
- Monitor seabird bycatch in key Namibian fisheries
- Access and collate FOA bycatch and mitigation compliance information for all key fleets (hake trawl and longline, monk trawl, midwater and pelagic longline).
- Work on improving data entry system within the MFMR
- Press to secure permanent place and at least annual discussion of seabird bycatch issues, particularly related to MSC conditions of the hake fisheries
- Carry out advocacy with MFMR with support from NNF
- Take targeted action to address compliance concerns in the hake longline fishery
- Continue to support improved relations with the Fisheries Inspectorate
- Deliver two seabird bycatch trainings (in Walvis Bay and Lüderitz) for observers, inspectors, fleet managers and shore skippers
- Improve sustainability of seabird bycatch mitigation interventions in key institutions
- Maintain a watching brief on Meme Itumbapo’s partnership with Walvis Traw
One Ocean Hub
Project Name: One Ocean Hub - Strengthening the effective management of the Namibian Islands Marine Protected Area (NIMPA) and expansion of the Marine Protect Areas network in Namibia
Project Donor: One Ocean Hub
Partners: Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources and, The Fisheries Observer Agency, and Southern Atlantic and Environmental Institute (SAERI), Overseas Development Institute (ODI)
Starting date: 01 July 2021 to 30 June 2022
Goal: To advance understanding of the value of ecosystem services in Namibia’s exclusive economic zone, in order to inform the sustainable implementation of Namibia’s Blue Economy plan as well as appropriate MPA designation and management.
Objectives:
- Develop a more in-depth understanding of the value of the natural environment to Namibia’s blue economy
- Understand the key trade-offs between different blue economy development decisions and, in doing so, build capacity to further evaluate these trade-offs for Namibia.
- Provide an additional layer of information to guide MPA designation and management
Shark Conservation Fund
Project Name: Shark Conservation Fund - Assessing the diversity and status of elasmobranchs in Namibia
Project Donor:
Partners: Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources and, The Fisheries Observer Agency
Starting date: 17 January 2022 – 16 January 2023
Goal: To have a baseline understanding of the impact fisheries have on elasmobranch populations and species most vulnerable to bycatch in Namibian fisheries is urgently needed, as well as a protocol that allows for the collection of effort-based catches, to species level, of all elasmobranchs.
Objectives:
- Conduct a preliminary assessment of the species caught in two industrial fisheries, and generate a species list
- Create ID guide for elasmobranchs encountered in Namibian fisheries
- Create data collection protocol to enable the collection of elasmobranch bycatch data for all fisheries
- Train observers in species identification and data collection
- Implement data collection in at least two fisheries using fisheries observers
- Develop suggestions for the NPOA-Sharks and Namibian Islands Marine Protected Area (NIMPA) management plan
Blue Marine
Project Name: Blue Marine - Securing the Namibian Islands’ Marine Protected Area
Project Donor: Blue Marine Foundation, and
Partners: Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources
Starting date: 01 January 2020 to 31 December 2022
Goal: To initiate and support the development of a Management Plan for the Namibian Islands Marine Protected Area and its implementation.
Objectives:
- Initiate and develop a collaborative Management Plan for the Namibian Islands Marine Protected Area.
- Mobilize resources towards the implementation of the Namibian Islands Marine Protected Area.
- Support priority actions under the Namibian Islands Marine Protected Area Management plan.
Independent Baseline Description of the Walvis Ridge
Project Name: Independent Baseline Description of the Walvis Ridge
Project Donor: Blue Marine Foundation
Partners: Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources and, The Fisheries Observer Agency
Starting date: 27 April 2022 to 27 July 2022
The key project objectives are to:
- Undertake a Rigorous Independent Baseline Description from literature and mined data sources.
- Undertake a stakeholder mapping and analysis to ascertain international and in-country stakeholders that should be engaged in any policy that is developed relating to the Walvis Ridge.
Fresh Water and Inland Fisheries
Strengthening Community Fisheries in KAZA
Title: Strengthening Community Fisheries in KAZA
Funding: European Union (EU)
Partners: Government Fisheries Department (Zambia), Okavango Research Institute, University of Namibia.
Date: 2020-2023
Contact person: Britta Hackenberg This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
To strengthen fisheries management in the KAZA region through ecosystem-based adaptation enhancing the socio-ecological resilience of communities.
Transboundary Fisheries Restoration
Title:Transboundary Fisheries Restoration
Funding: Peace Parks Foundation (PPF)
Date: 2019-2022
Contact person: Britta Hackenberg This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
To contribute to the recovery of the transboundary fishery resource in focal communities along the Zambezi and Chobe, within the Zambian Stratum V so that residents have a secure source of protein and fishing remains an important part of the social fabric.
Support to Community Fisheries
Title: Support to Community Fisheries
Funding: The Nature Conservation (TNC)
Date: 2021-2022
Contact person: Britta Hackenberg This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
Implementing a suite of community-led freshwater and fisheries conservation interventions and management activities designed to improve the livelihoods of the local communities while also conserving vital freshwater ecosystems in the upper catchment of the Okavango river basin in Angola and along the border between Namibia and Angola.
Implementing an integrated approach to Natural Resource Management in the Middle Cubango-Okavango Basin to mitigate land degradation
Title: Implementing an integrated approach to Natural Resource Management in the Middle Cubango-Okavango Basin to mitigate land degradation
Funding: European Union (EU)
Date: 2021-2022
Contact person: Britta Hackenberg This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Objective:
- To strengthen land management through improved land use planning,
- Reduction of environmental degradation
- Consideration of ecological service provision, and Improved livelihoods
- Diversified opportunities and increased income:
- Increased knowledge of policies around degradation and biodiversity loss
- Establishment of a fish reserve
Completed Projects
Integrated Co-management Fisheries Resources
Funding: WWF Norway
Partners: Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources, NNF, WWF
Project dates: January 2010 to December 2012
Project details
The fish resources of the Zambezi and Chobe rivers and associated Caprivi floodplains are both a vital component of the livelihoods of the floodplain inhabitants and a major angling tourist attraction. Fish is thus a major contributor to food security and the local economy.
Improved communications in the area and consequent increased commercialization of the fishery were identified as a major threat to rural livelihoods and to aquatic biodiversity through over-exploitation of the larger fish species that are most valuable for both food and for angling tourism. Concerns were expressed by the local fishing communities and by the tourist organizations that the fishery was in serious decline as a result of widespread use of illegal and destructive fishing methods, and the results of monitoring programmes carried out since 1997 by the Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources confirmed over-exploitation of the large tilapiine cichlid species.
The Zambezi/Chobe fisheries project was thus conceived as a way of empowering the local communities to manage the resources in a sustainable way through the formation of local management committees and devolution of responsibility for management, as envisaged in the Namibian constitution and the Inland Fisheries White Paper. The project set out to facilitate the management of the fisheries by developing a system of integrated co-management and because the Zambezi fishery is a shared resource with Zambia, harmonization of activities and cooperation in surveys and monitoring. It has always been acknowledged that this type of activity requires a long-term commitment. After the first phase of the project ended in December 2009, the second phase ran from January 2010 to December 2012. Management of the project was shared between Mr. D. Tweddle as Project Executant and Dr. C. Hay as Project Co-executant.
Project outputs
Output 1: Cross-border collaboration achieved in the management of the fisheries resources.
Output 2: The management plan for the fisheries developed during Project Phase 1 was successfully implemented (in collaboration with neighboring countries) for the benefit of the communities.
Output 3: Fish Protection Areas established and fully functional in targeted pilot communities.
Output 4: Tourist angling lodges operating in agreement with local fishing/conservancy committees.
Output 5: Capacity built-in research and monitoring of fish resources.
Output 6: Collaboration in the next phase of the NNF fish ranching project.
NamPower/NNF Strategic Partnership
Funding: European Investment Bank (EIB), Nedbank Go Green Fund, Environmental Investment Fund (EIF) Namibia, NamPower
Partners: NamPower, Regional Electricity Distributors (REDs), other power utilities and a variety of stakeholders
Dates: 2008, ongoing
Location of the project: throughout Namibia
Contact persons: Mike & Ann Scott (email This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.)
Why an industry-conservation partnership?
Wildlife and electricity supply conflicts are costly both to industry and to our biodiversity. Inconvenient outages (blackouts) caused by wildlife interactions such as electrocutions and collisions and the nesting of birds on power line structures may result in high maintenance and repair costs, especially in terms of the impacts of Sociable Weaver nesting activity during the rainy season.
At the same time, 71 (10%) of Namibia’s 687 bird species are recognised as being under threat. About 75% of this group fall into one or more of the following groups: coastal and marine birds; scavenging birds; birds impacted by power lines; and wetland birds. Although information is still being gathered on the extent of the impacts of power supply structures on wildlife at present, in terms of collisions and electrocutions, these factors are emerging as a very real threat.
Many of these impacts could be reduced or prevented with appropriate communication, planning and management. Due to a growing concern about the above issues, the NamPower/Namibia Nature Foundation Strategic Partnership was launched in 2008, with generous funding by the European Investment Bank.
What is the purpose of the project?
The mission of the Partnership is to address wildlife and electricity supply interactions in Namibia.
What are the objectives? To:
- Monitor, report, research and manage electricity supply and wildlife interactions;
- Incorporate wildlife mitigation into existing electricity supply networks, and into the planning for future networks;
- Promote awareness, education, communication and collaboration about the risks that the electricity supply poses to wildlife, and wildlife to the electricity supply.
Project action plan
The above objectives are directly related to a dynamic project action plan, developed and updated regularly in consultation with stakeholders.
How you can become involved
- We need your help to build our database of relevant information that is the basis of our dynamic, web-based Environmental Information Service (EIS) for Namibia (see www.the-eis.com).
- We specifically need information and photographs on wildlife and electricity supply interactions (e.g. mortalities or injuries due to collisions or electrocutions; nesting or roosting etc. on electricity supply structures in your area). Please use the Field Investigation Form to record this information.
- Subscribe and contribute to the Partnership's free, electronic newsletter
Project Action Plan for the NamPower/Namibia Nature Foundation Strategic Partnership
- Conduct power line surveys/monitoring
1.1 Conduct power line surveys/monitoring
1.2 Enter/process/analyse/provide feedback on data
2. Implement effective mitigation
2.1 Implement proactive mitigation measures for new electricity supply structures
2.2 Implement mitigation for existing electricity supply structures
2.3 Support monitoring/mitigation in renewable energy developments
3. Conduct focal research projects
3.1 Research and implement mitigation for impacts of weaver nesting on electricity supply structures
3.2 Bustard and power lines project
3.3 Flamingo tracking project
3.4 Investigate sources of bias in data gathering
- Promote awareness, information-sharing, education, outreach, collaboration
4.1 Produce newsletters and media releases
4.2 Produce further project information: flyer; website; guidelines
4.3 Disseminate information and material to identified target groups
4.4 Encourage further communication/collaboration with local partners
4.5 Encourage further communication/collaboration with international partners
4.6 Conduct training/awareness workshops and other workshops
4.7 Support and promote a free online Environmental Information Service (EIS)
Newsletters:
NP/NNF Newsletter No1 (Jun 2009)
NP/NNF Newsletter No2 (Oct 2009)
NP/NNF Newsletter No3 (Feb 2010)
NP/NNF Newsletter No4 (Jun 2010)
NP/NNF Newsletter No5 (Sep 2010)
NP/NNF Newsletter No6 (Feb 2011)
NP/NNF Newsletter No7 (May 2011)
NP/NNF Newsletter No8 (Sep 2011)
NP/NNF Newsletter No9 (May 2012)
NP/NNF Newsletter No10 (Nov 2012)
NP/NNF Newsletter No11 (Mar 2013)
NP/NNF Newsletter No12 (Oct 2013)
NP/NNF Newsletter No13 (Apr 2014)
NP/NNF Newsletter No14 (Nov 2014)
NP/NNF Newsletter No15 (Apr 2015)
NP/NNF Newsletter No16 (Nov 2015)
NP/NNF Newsletter No17 (Oct 2016)
Downloads:
Wildlife/Power Line Incident Form
Stories:
The NamPower/NNF Strategic Partnership - A Groundbreaking Alliance
For further information or to report wildlife and power supply incidents, please email Mike and Ann Scott at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..


